A brushless direct current motor (BLDC: Brushless Direct Current Motor), also known as an electronic commutation motor (ECM or EC motor) or synchronous DC motor, is a synchronous motor that uses direct current (DC) power supply. The brushless DC motor is essentially a permanent magnet synchronous motor that adopts DC power input and becomes a three-phase AC power supply with an inverter.
There are various types of motors, and brushless DC motors are the most ideal speed control motors today. It integrates the advantages of DC motor and AC motor, not only has the good adjustment performance of DC motor, but also has the advantages of simple structure of AC motor, no commutation spark, reliable operation and easy maintenance. Therefore, it is well received by the market and is widely used in automobiles, home appliances, industrial equipment and other fields.
Development history of brushless DC motors
DC brushless motor is not the earliest product, but developed on the basis of brushed motor, and its structure is more complex than that of brushed motor. DC brushless motor is composed of motor body and driver, different from brushed DC motor, brushless DC motor does not use mechanical brush device, but adopts square wave self-controlled permanent magnet synchronous motor, and replaces the carbon brush commutator with Hall sensor, and uses NdFeB as the permanent magnet material of the rotor.
However, as early as the last century, when the motor was born, the practical motor produced was in the form of brushless.
1740s: The invention of the electric motor begins
Through the work of Scottish Benedictine monk and scientist Andrew Gordon, early models of electric motors first appeared in the 1740s. Other scientists, such as Michael Faraday and Joseph Henry, went on to develop early electric motors, experimenting with electromagnetic fields and discovering how to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
1832: Invention of the first commutator DC motor
In 1832, the British physicist William Sturgeon invented the first DC motor that could provide enough power to drive machinery, but its application was severely limited due to its low power output.
1834: The first real motor is manufactured
Following in Sturgeon’s footsteps, Thomas Davenport of Vermont, USA, made history by inventing the first official battery-powered motor in 1834. It was the first electric motor with enough power to perform the task, and his invention was used to power small printing presses. In 1837, Thomas Davenport and his wife, Emily Davenport, obtained the first patent for a DC motor.
But their motor design still faced the same power and efficiency issues as William Sturgeon’s design. Unfortunately, Thomas went bankrupt due to the high cost of battery electricity involved, and the machine could not be used commercially.
Thomas and Emily Davenport’s patented motor
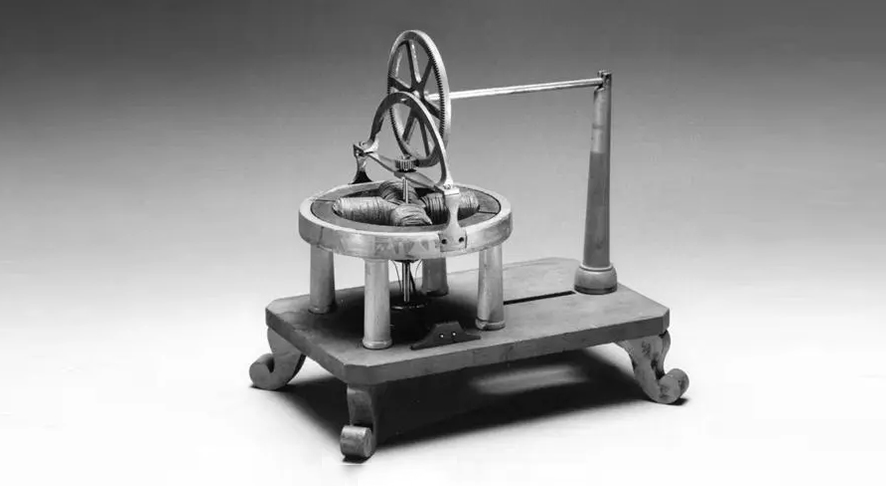
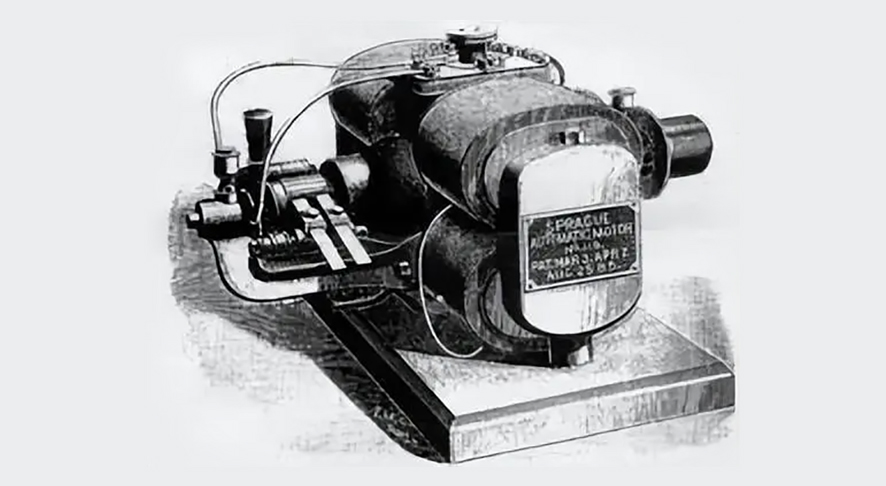
1886: Invention of the practical DC motor
In 1886, the first practical DC motor that could operate at a constant speed at variable weight was introduced. Frank Julian Sprague was its inventor, and it was this motor that provided the catalyst for the widespread use of motors in industrial applications.
Frank Julian Sprague’s “practical” motor
It is worth mentioning that the practical motor adopts a brushless form, that is, an AC squirrel cage asynchronous motor, which not only eliminates the voltage loss at both ends of the spark and winding, but can deliver power at a constant speed. However, asynchronous motors have many insurmountable defects, and the development of telephone technology is slow.
Shortly after the birth of brushless motors, people invented brushed DC motors. DC brush motor has become the mainstream at that time once it came out because of its simple mechanism, easy production and processing, convenient maintenance and easy control.
1887: The AC induction motor is patented
In 1887, Nikola Tesla invented the AC induction motor and successfully patented it a year later. It was not intended for road vehicles, but was later modified by Westinghouse engineers. In 1892, the first practical induction motor, followed by a rotating bar winding rotor, made the motor suitable for automotive applications.
1891: Development of three-phase motors
In 1891, General Electric began developing three-phase induction motors. To take advantage of the wound rotor design, GE and Westinghouse signed a cross-licensing agreement in 1896.
1955: The era of brushless DC motors begins
In 1955, D. Harrison and others in the United States first applied for a patent for replacing the mechanical brushes of brushed DC motors with transistor commutation lines, officially marking the birth of modern brushless DC motors. However, at that time, there was no motor rotor position detection device, and the motor did not have the ability to start.
1962: Invention of the first brushless DC (BLDC) motor
Thanks to advances in solid-state technology in the early 1960s, in 1962, TG Wilson and PH Trickey invented the first brushless DC (BLDC) motor, which they called “DC motors with solid-state commutation.” The key element of a brushless motor is that it does not require a physical commutator, making it the most popular choice for computer disk drives, robots, and airplanes.
They used Hall elements to detect rotor position and control winding current commutation, making brushless DC motors practical, but limited by transistor capacity, the motor power is relatively small.
1970s to present: Brushless DC motor applications develop rapidly
Since the 70s, with the emergence of new power semiconductor devices (such as GTR, MOSFET, IGBT, IPM), the rapid development of computer control technology (single-chip microcomputer, DSP, new control theory), and the advent of high-performance rare earth permanent magnet materials (such as samarium cobalt, NdFeB), brushless DC motors have developed rapidly and the capacity has been increasing.
Later, with the launch of Mac classic brushless DC motors and their drivers in 1978, and the research and development of square wave brushless motors and sine wave brushless DC motors in the 80s, brushless motors really began to enter the practical stage and developed rapidly.
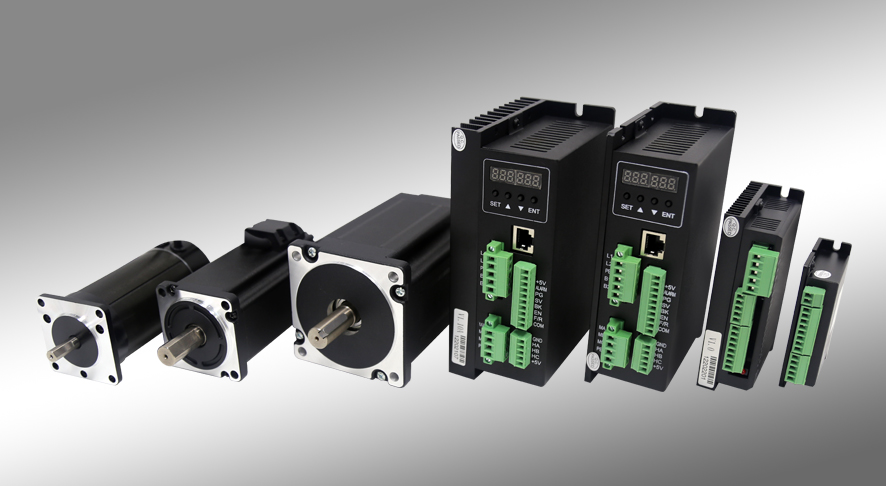
Since its establishment, Shenzhen Zhongling Technology Co., Ltd. has been focusing on the research of servo motors and brushless motors, and has obtained a number of patents with rich experience. The servo motors and brushless motors produced by the company are also sold at home and abroad, becoming the best choice for many robot companies and many automation equipment manufacturing companies.
Post time: May-24-2023